- Engineering. Made in Germany.
- SPAX - we care.
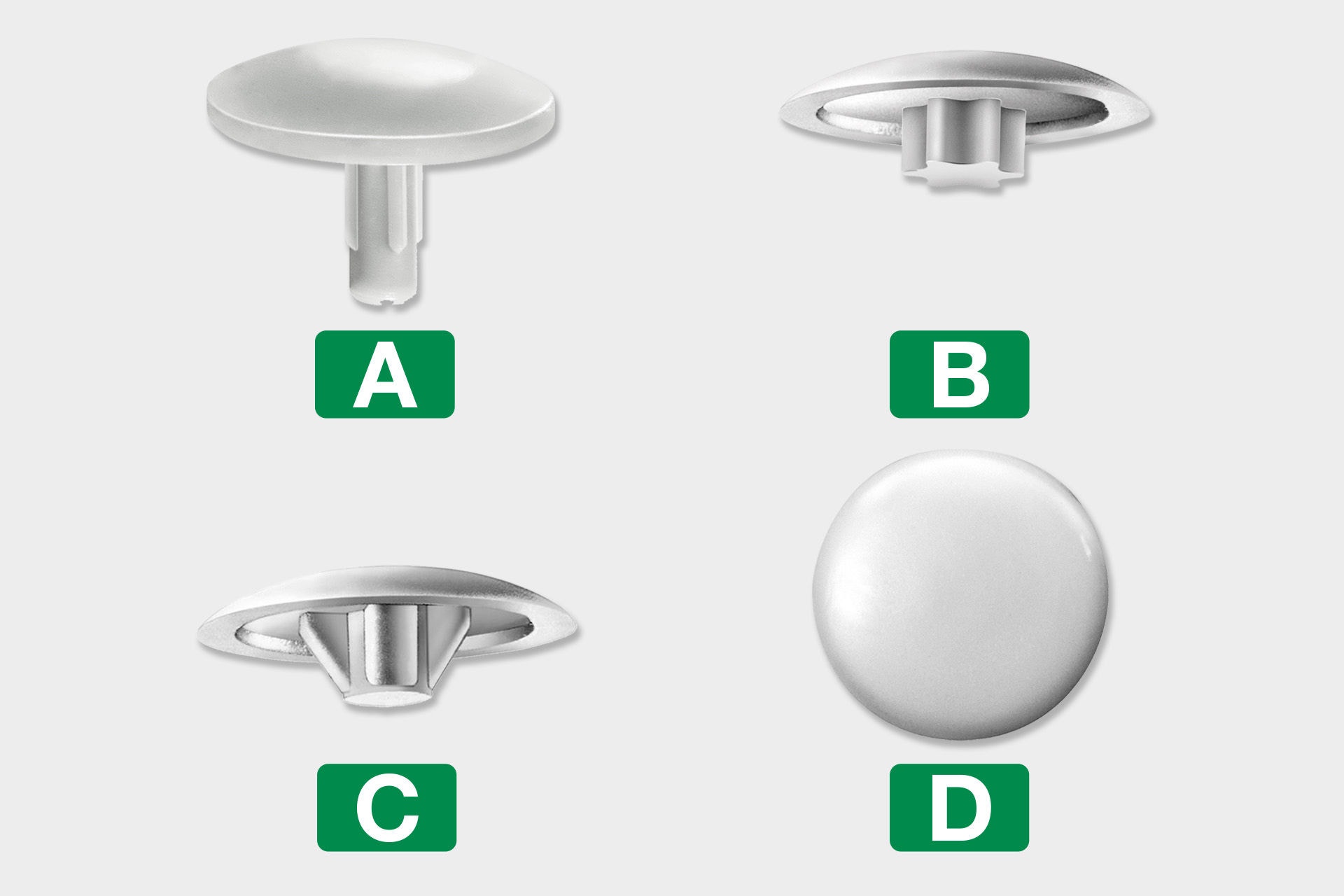
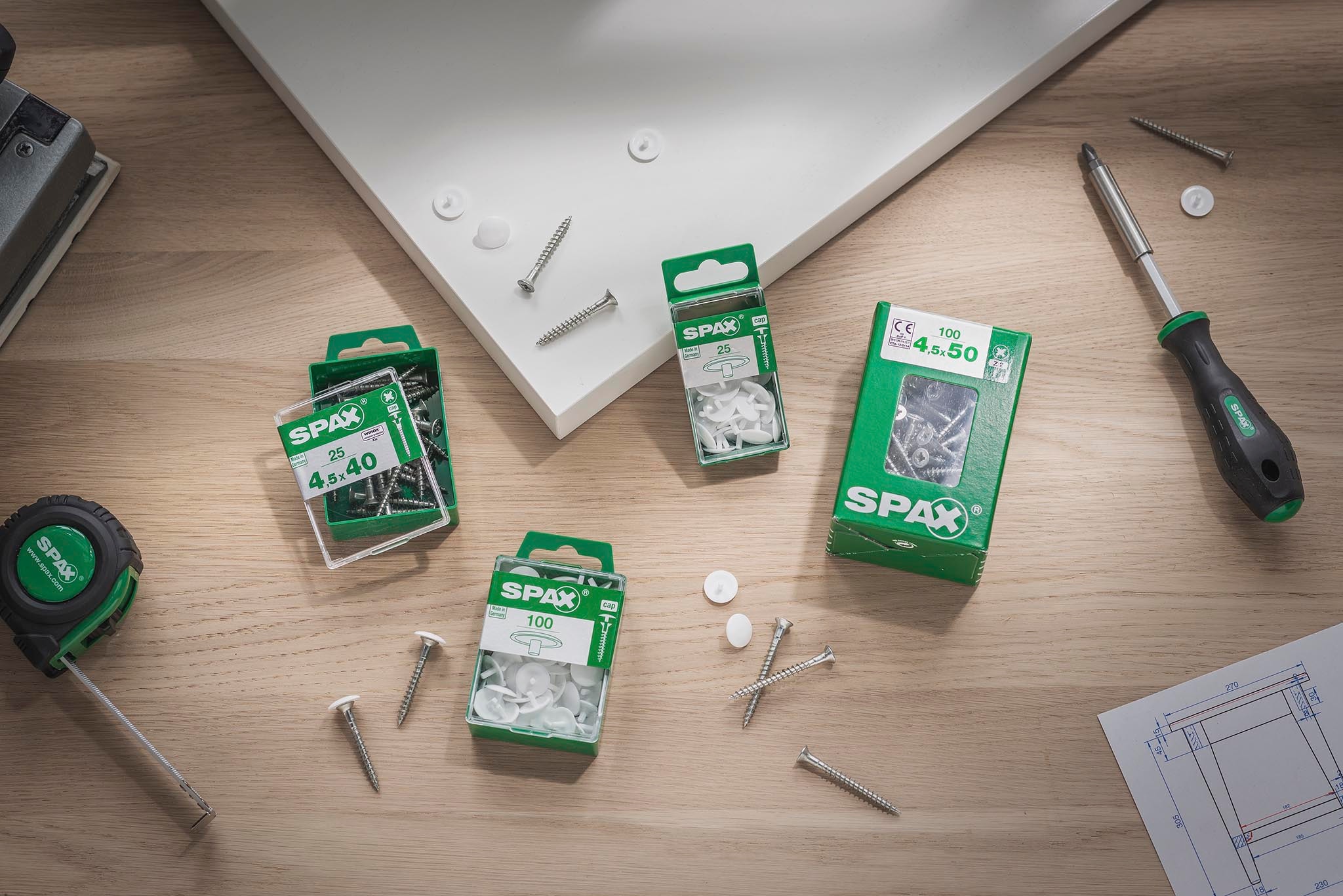
The practical cover caps make unwanted screw heads disappear in a flash. Simply insert the appropriate cover cap into the force attack, the head bore or, in the case of the frame anchor, on the head of the screw. As a result, the screw connection becomes almost invisible.
Our range includes the most common surface colours.
There are the following types of cover caps in the SPAX range:
A) Caps for head hole drilling
B) Caps for T-STAR plus
C) Caps for Pozi
D) Caps for SPAX-RA
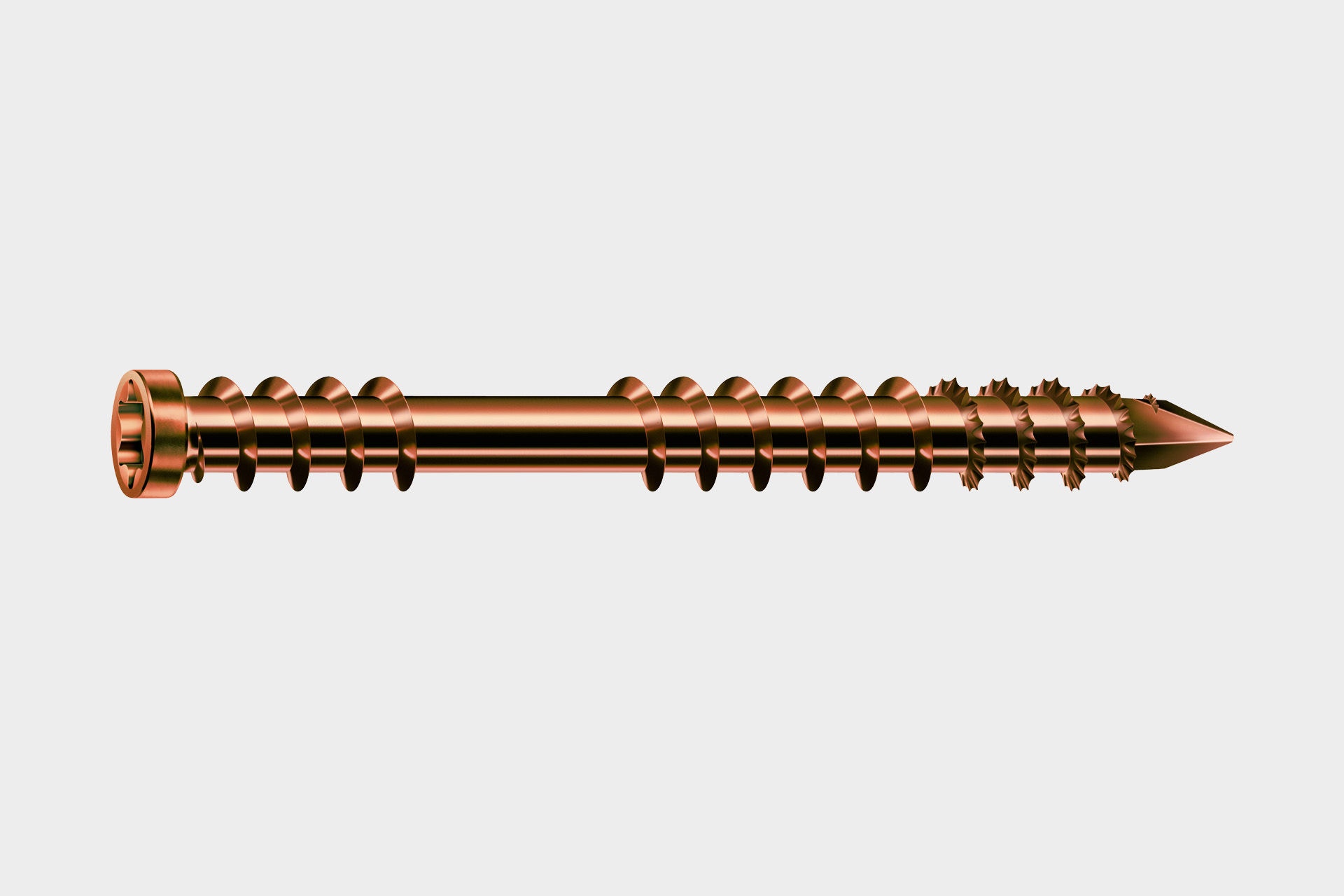
Antique Spax screws are made of stainless steel. They get their brownish colour through a thermal process. Due to the use of stainless steel, the screw has increased corrosion resistance and is ideal for outdoor use, e.g. in terrace or façade construction.
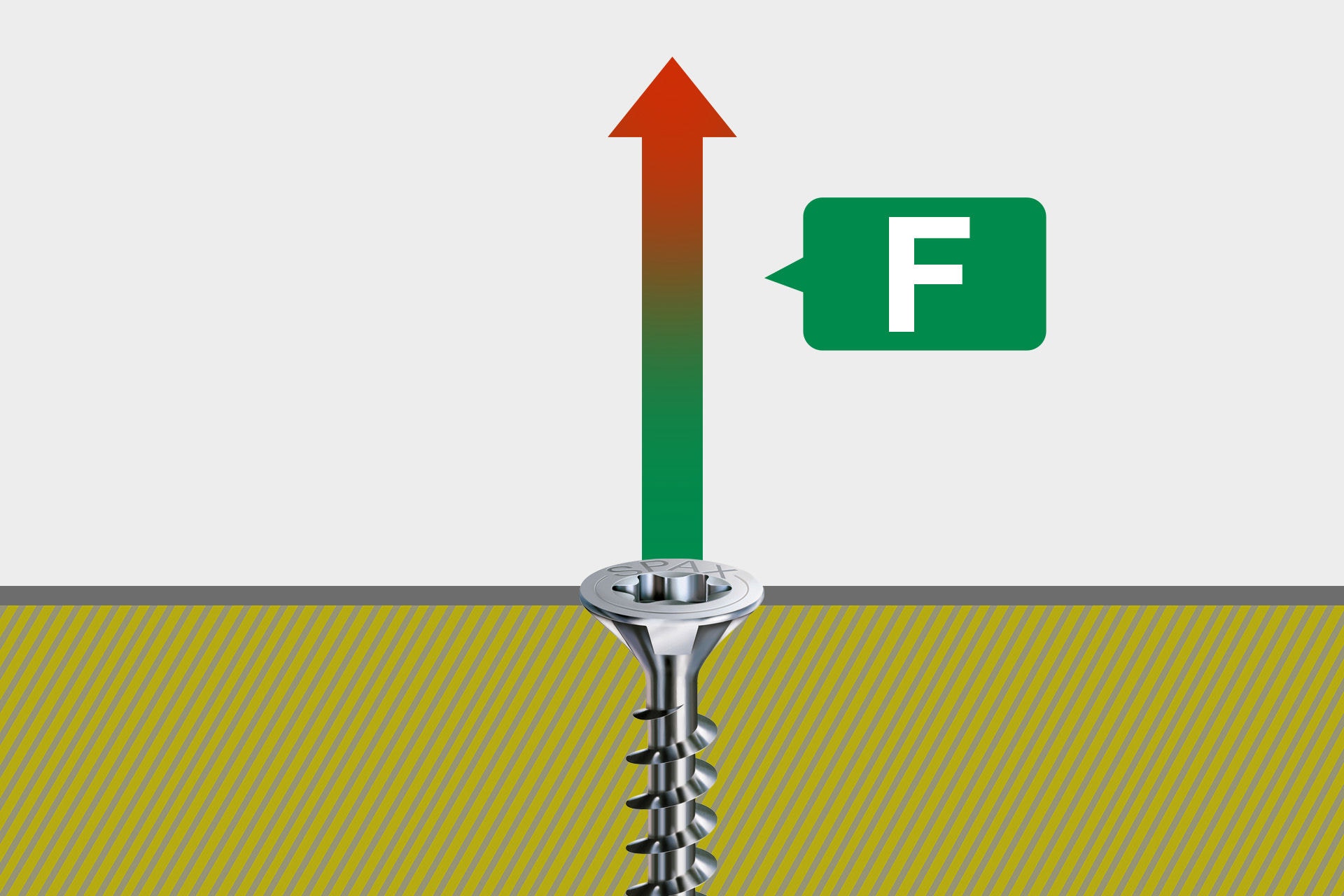
The pull-out force refers to the necessary force that must be applied to tear a screw out of its anchorage. It depends on several factors, such as screw geometry, screw-in depth, material used, thread length
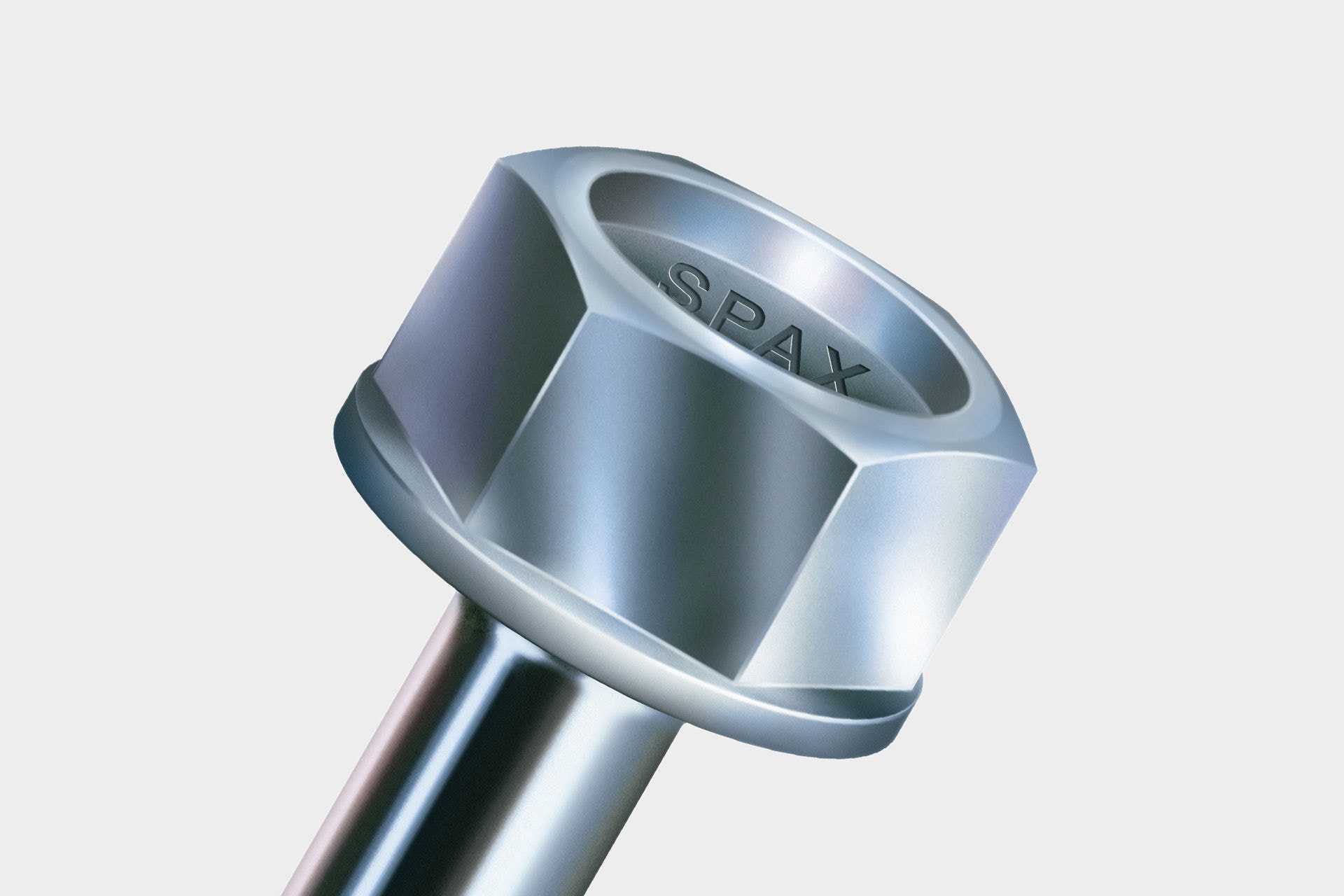

A head with an outer hexagon has no recess for a screwdriver blade and is tightened with a spanner or ring wrench or a corresponding socket. This head shape can be found on SPAX threaded rods.

Austenite is the main structural component of many stainless steels. Unlike many other steels, it has no magnetic properties.
It differs from martensichtischer steels (also stainless, but magnetic) in that it is no longer hardened and thus has a higher corrosion resistance. For more information, see "Stainless Steel".
A bit is a small interchangeable screwdriver blade without a handle. They are available in many different designs for every conceivable form of force attack. Due to their hexagonal design in the rear area, they can be easily inserted into the matching bit holder. This saves you from carrying many different screwdrivers and still has the right tool with you.
These are available in blade sizes T10 to T50. The SPAX bits T-STAR plus ensure better power transmission to the screw, longer service life and improved fit and guidance of the screw.

Screws that have a drill tip have a particularly pronounced tip . It is based on that of a drill and has two small cutting edges. This makes the screw particularly suitable for fastening metals and plastics. Due to their boron tip, they are particularly suitable for attaching fittings to window profiles with metal reinforcement.

Brake ribs are small, wedge-shaped elevations under the countersunk head. They brake the screws when they are placed on a metal fitting. This effectively prevents overtightening of the screw, ensuring a solid connection between metal fitting and component.

Burnished screws are made of steel whose surface has been refined by a chemical process. This surface has a lower corrosion resistance compared to a galvanized screw and should only be used indoors. Burnished screws have a brownish appearance and are therefore ideal for applications in furniture restoration with dark or antique woods.
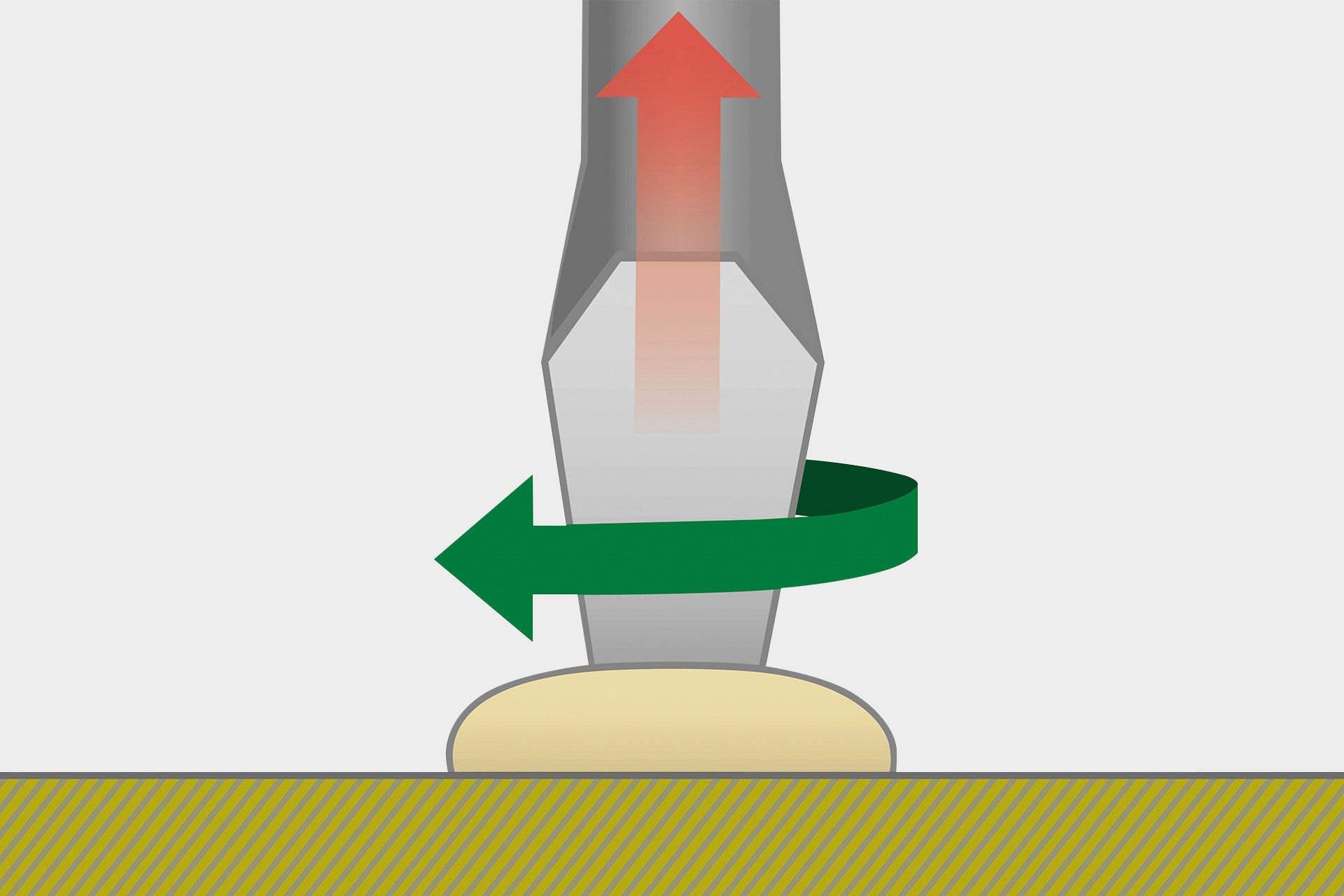
With conventional, conical force attacks such as the cross slot, there is basically the problem that the torque exerted by the user pushes the screw blade out of the force attack upwards. This often results in the blade slipping or even the complete destruction of the force attack (it is also said that the screw was turned "round"). In order to counteract this slipping, the user must exert a contact force. By using a force attack with a parallel profile (such as the T-STAR or the T-STAR plus), the unwanted cam-out effect and the application of contact force is eliminated. "Round-turned screws" are a thing of the past.

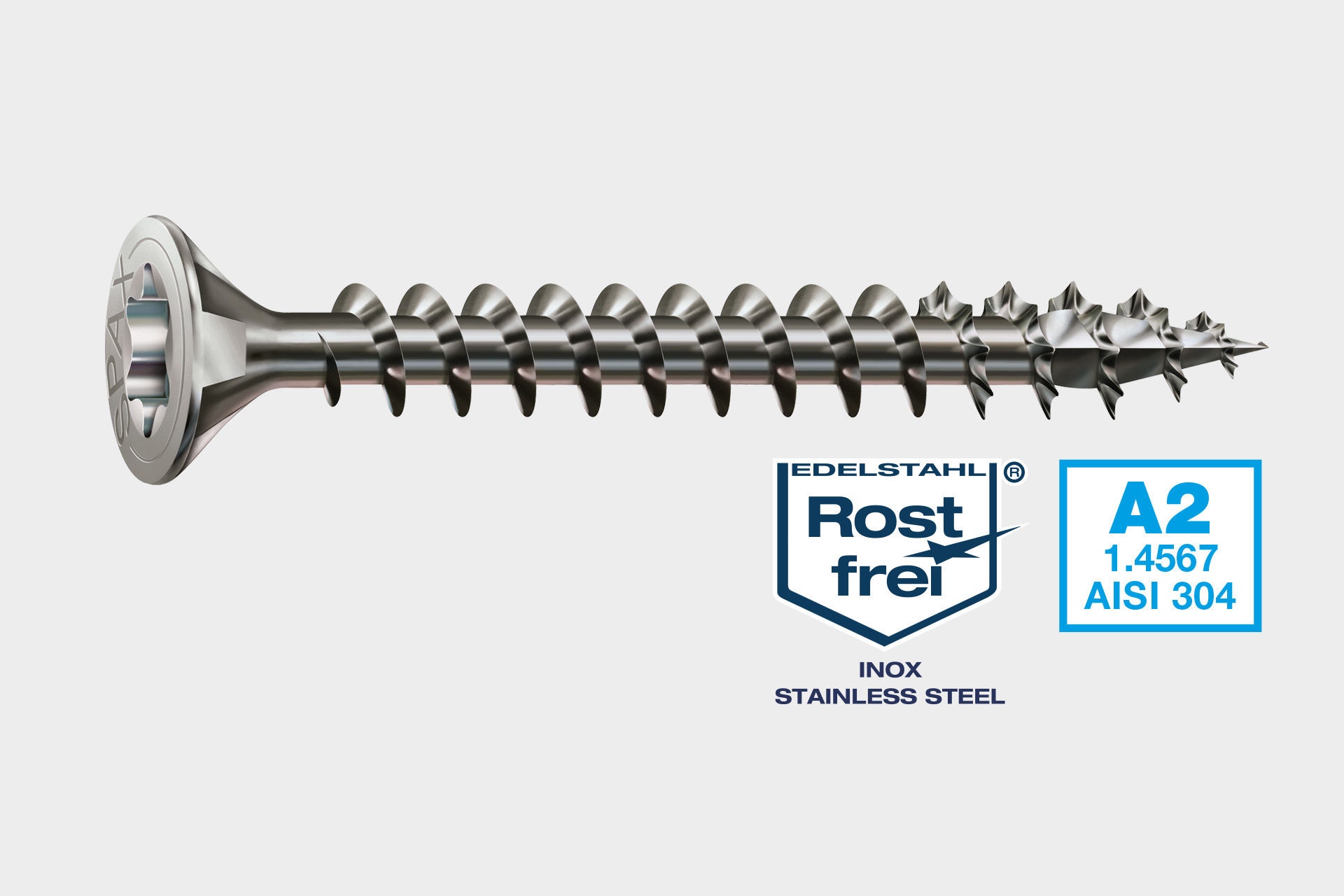
SPAX stainless steel are particularly suitable for outdoor use and damp rooms. They are available in stainless steel A2 for outdoor applications where they are exposed to direct weather conditions, as well as for use in damp rooms (e.g. kitchen and bathroom). For applications in coastal areas, we recommend the version in stainless steel A4. Stainless steel is characterized by a high chromium content. This forms a protective layer on the material surface. Other alloying components such as nickel, molybdenum, manganese and niobium lead to even better corrosion resistance.
Austenite is the main structural component of many stainless steels. It is not magnetic.
Stainless steels:
Material number | Designation |
1.4016 | Stainless steel A1 |
1.4567 | Stainless steel A2 |
1.4578 | Stainless steel A4 |
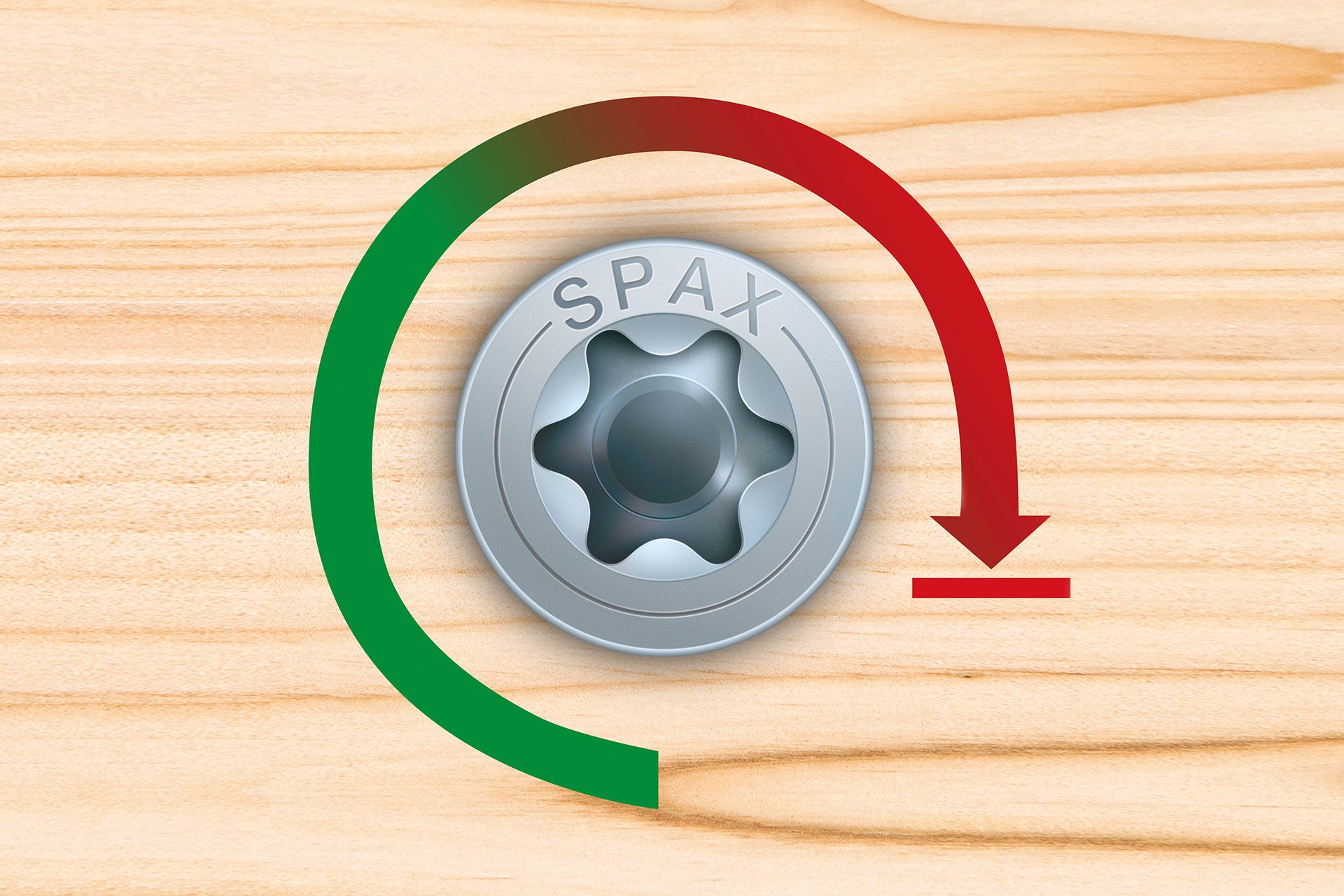
The screw-in torque describes the force required to screw the screw into the carrier material. Through special coatings, pre-drilling or, of course, by means of the key features of our SPAX, the shaft profile, the milling cutter with 4CUT and the tip with 4CUT, it is possible to reduce the screw-in torque in order to enable fatigue-free work.
The FEX screws have been specially developed for the production of windows. With these, SPAX offers a closed range of screws for a wide variety of applications in window construction. The range of FEX is divided as follows:

FEX: the fitting screw
Is suitable for attaching fittings to wooden profiles, as well as to plastic profiles without steel reinforcement. Thanks to its CUT tip, it effectively reduces the formation of gaps in wooden profiles.

FEX-A: the window drill screw
Is suitable for attaching steel reinforcement to plastic profiles as well as for mounting fittings on single-walled plastic profiles with steel reinforcement. Thanks to its drill bit, it ensures optimum drilling performance, both in manual and automatic operation.

FEX-KS: the screw
Has been developed for the attachment of fittings to plastic profiles without steel reinforcement. Due to its special geometry, it can be processed without pre-drilling the plastic and ensures a solid hold.

FEX-RS: the roller shutter screw
Has been specially developed for the fastening of roller shutter profiles. Despite its short size and thickness, the screw does not need to be pre-drilled. A special needle tip allows a clean and fast screwing in of the screw. The screw is available for the most common profiles.

FEX-H: the wooden window screw
Has been developed for fixing window fittings in classic wooden window frames. It impresses with a 4CUT tip which offers a clean and easy penetration into the wood and reduces the screw-in torque.
FEX: Combi screw
Has been developed for the fastening of fittings and corner bearings for fastening in plastic windows with steel reinforcement. It impresses with a drill tip and two consecutive thread types. In the upper area it has a coarse thread (for plastic) in the lower area a fine thread (for metal).
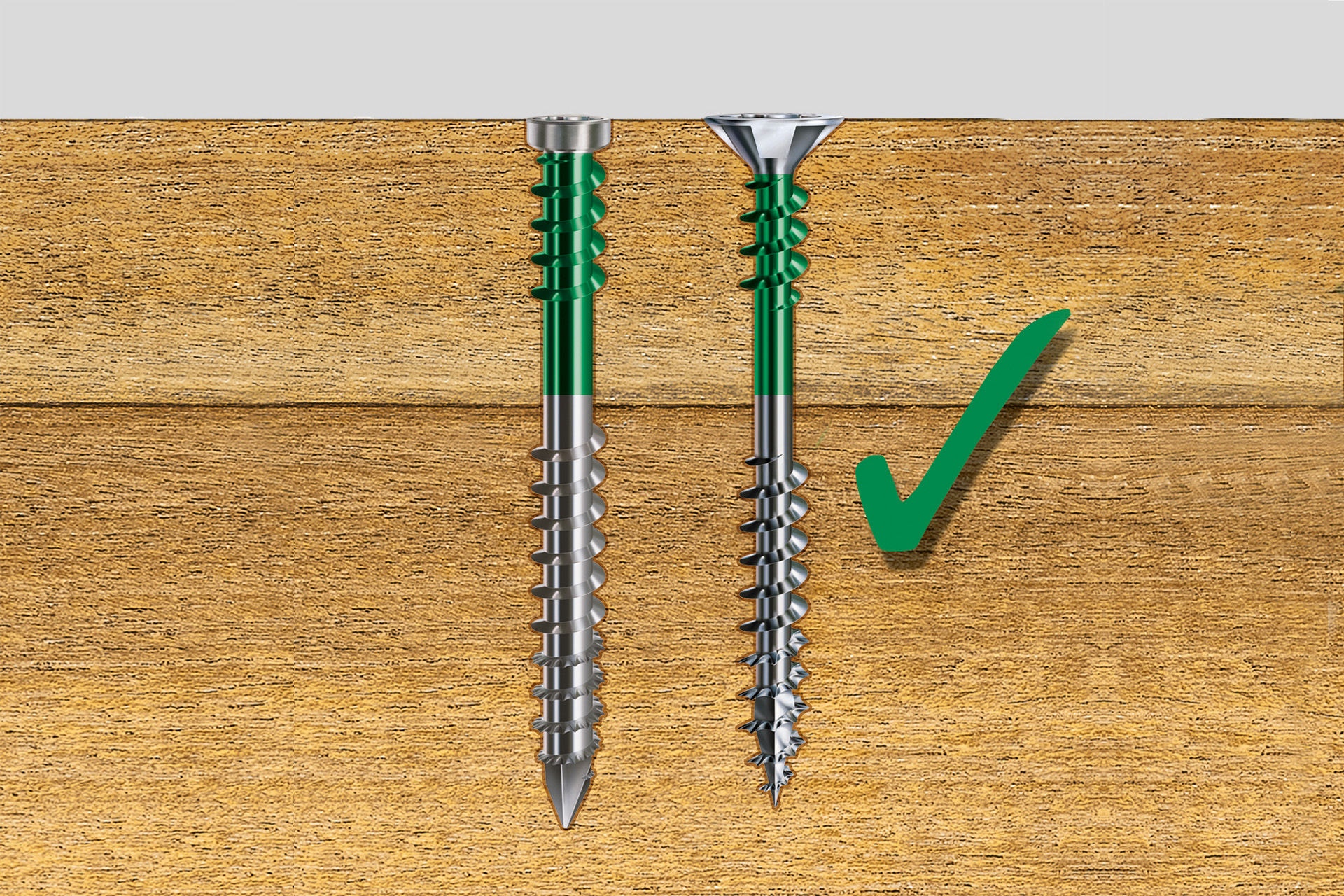

The fixing thread is a second thread just below the head of the SPAX. The fixing thread guarantees a secure and permanent connection of two woods. Especially when laying wooden floors indoors with the SPAX installation screw or when building wooden terraces outdoors with SPAX-D in stainless steel, the fixing thread holds the cover board permanently on the substructure. Creaking noise of the floor construction is thus minimized.
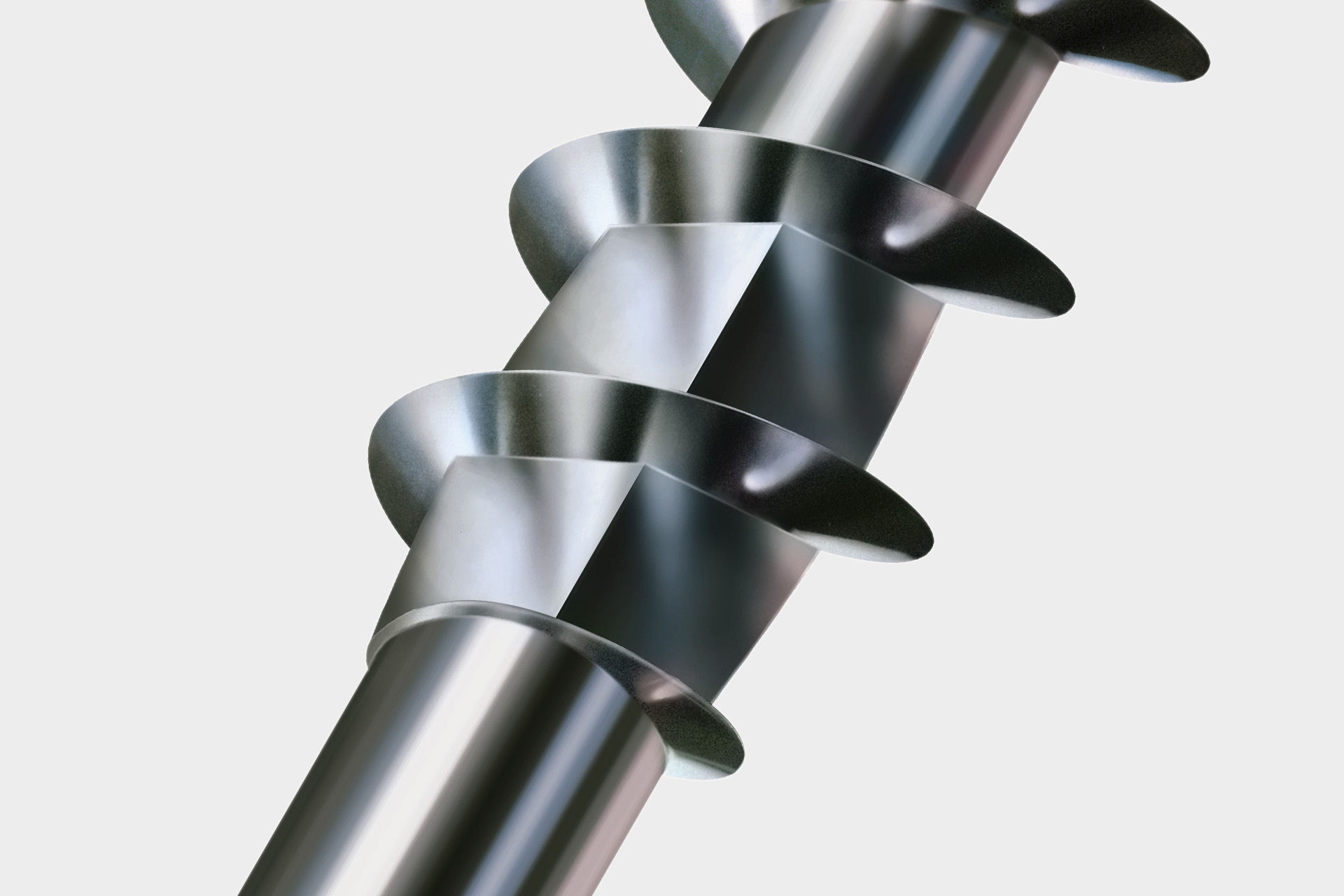

Cutter with 4CUT: 4CUT is the square shape of a SPAX in the transition from the thread to the shaft. Its advantage is the reduction of screw-in torque by up to 60 percent. Thus, the SPAX can be processed evenly and with little effort; the energy reserves of a battery-powered tool are also spared. As a rule, the 4CUT is used for screw lengths from 160 mm.
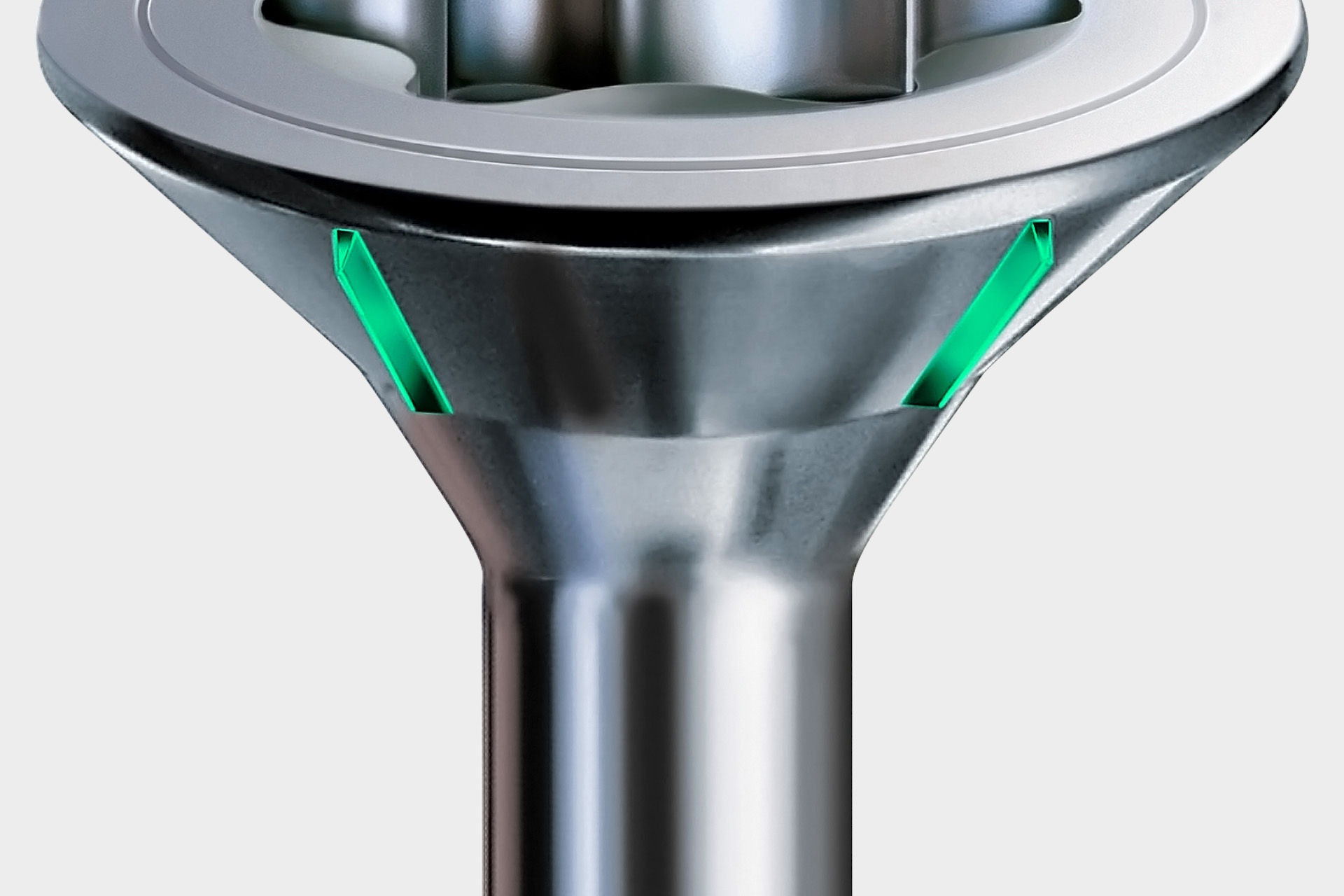

Milling ribs are wedge-shaped elevations under the countersunk head of the SPAX. As soon as the screw head hits the surface of the wood, the milling ribs unfold their effect: a clean and flush sinking of the head is possible!
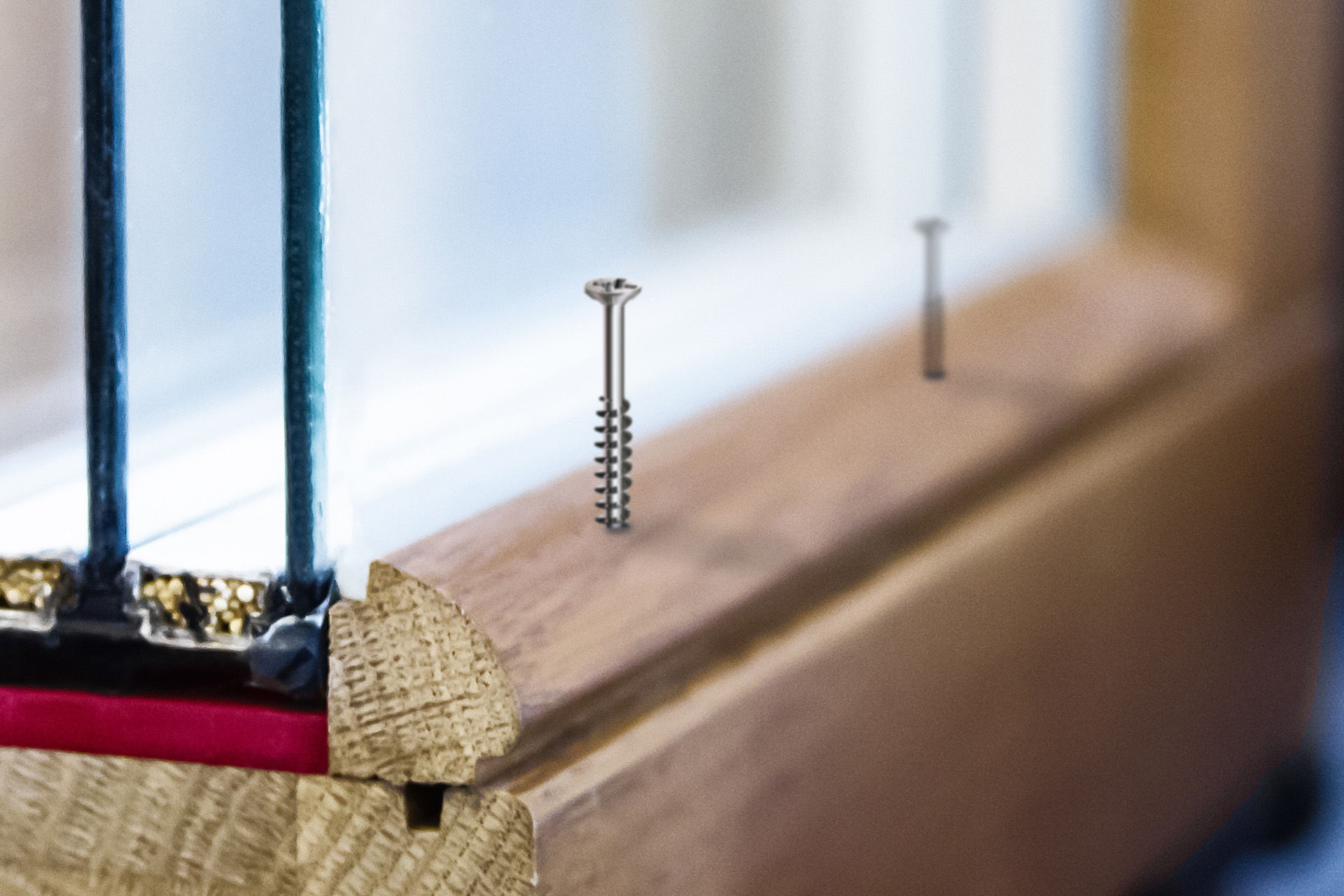

A glass strip is the strip inside a window frame. It serves to fix the window in the frame and allows a defective window to be dismantled and replaced without great effort.

Each SPAX is coated with a sliding coating , which allows a smoother screwing in of the screw. This results in a reduction of the forces to be applied and the screw-in torque is reduced. Above all, this protects the battery charges of a screwdriver, and ensures a higher throughput of screws per battery charge.

The semicircular head (also panhead) is an almost spherical shape of the screw head. This head version is ideal for the visible attachment of metal fittings to wood.
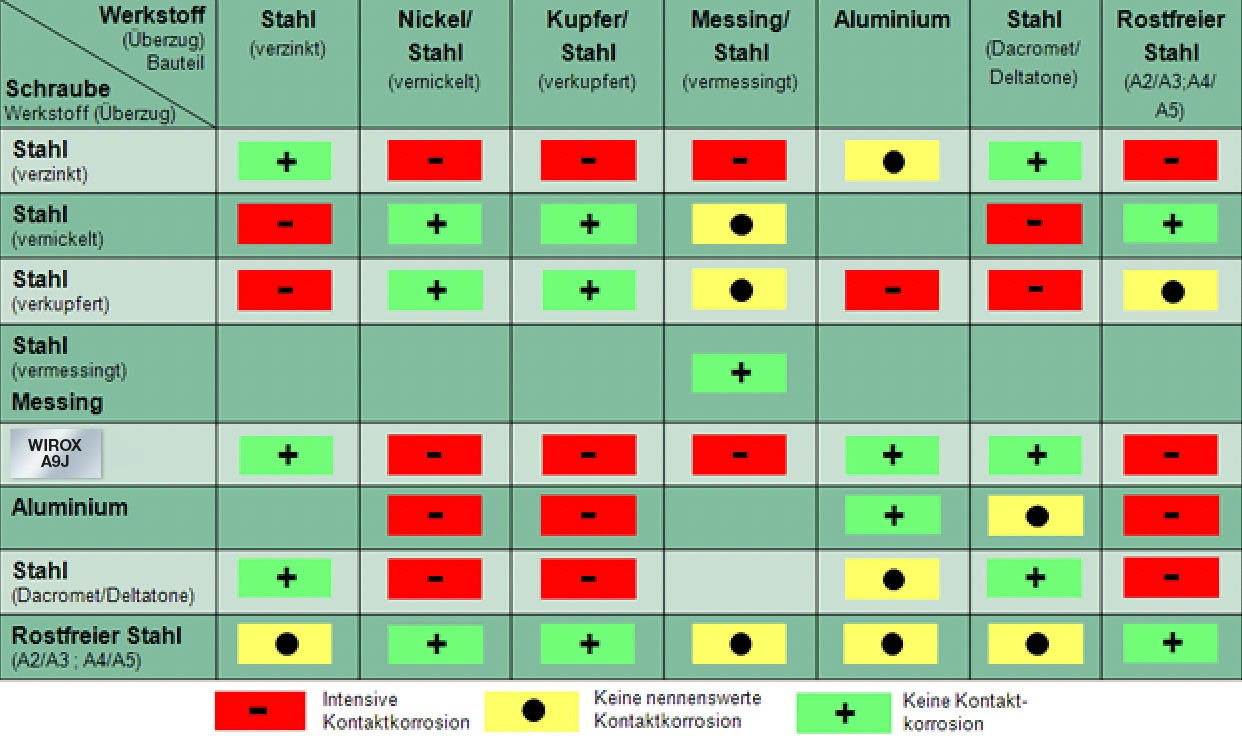
Contact corrosion can occur when different precious metals are in close contact. For example, a stainless steel screw is screwed to a galvanized sheet steel. The nobler metal then promotes corrosion (rusting). This results in a so-called contact corrosion. The prerequisite for this process is a corrosive medium between the two metals, such as water or simply normal humidity.
The attached table shows different combinations of materials and their compatibility under the aspect of contact corrosion.
Corrosion (from Latin corrodere = "gnawing") is the reaction of a material with its environment. Corrosion occurs, for example, on metals and causes a measurable change in the material, so that the function of the component can be impaired. The best-known type of corrosion is rusting, i.e. the oxidation of iron. Corrosion resistance in the SPAX is the protection against "rust".
Anti-corrosion code | Surface |
A3J | WIROX |
A2L | YELLOX |
A2J | Zinc transparent |
A3L | Zinc yellow |
A9J | WIROX |
P3J | WIROX |
C1A | Browned |
E1J | Nickel-plated |
D1U | Brass-plated |
1st place: coating metal
2nd place: medium layer thickness of the coating
3rd place: gloss level and post-treatment
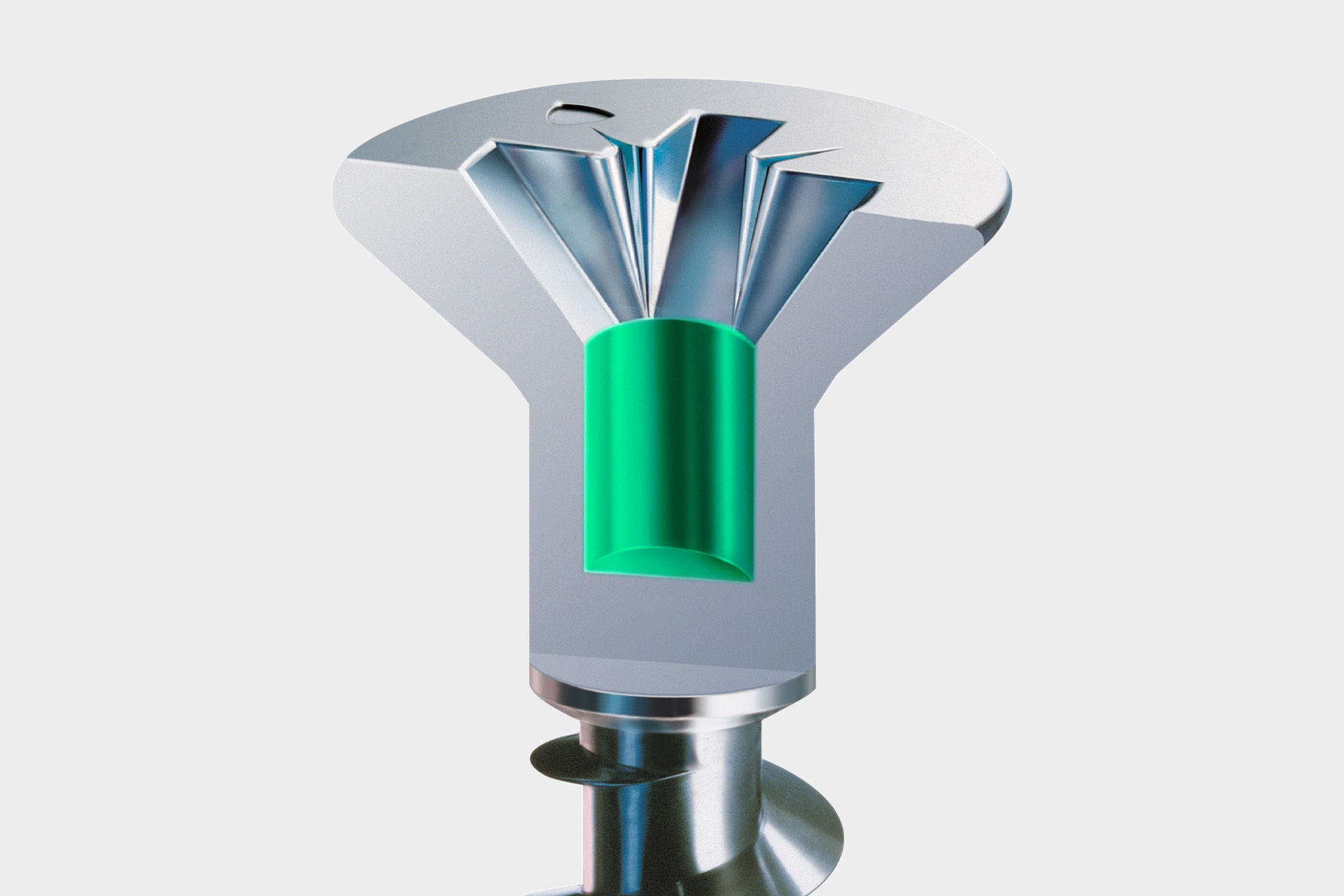

Head hole drilling describes the pin-shaped depression that connects to the force attack within the screw head. Due to the hole, special cover caps for this type of screw hold particularly well and are secured against falling out.

The force attack (also called drive) is located in the screw head. The shaping of this serves to pick up the bit or blade of the screwdriver and thereby enables a power transmission between screw and blade. Only through this can a screw be screwed in and out.
1. The cross-force attack developed by Phillips offers the advantage compared to the simple slotted force attack that it reduces the risk of lateral slipping out of the tool blade and thus damage to the workpiece. Due to the tapering of the flanks in the cross slot, however, an axial force occurs when tightening the screw, which pushes the blade out of the force attack (cam-out effect). This force attack is used in window construction screws (FEX).
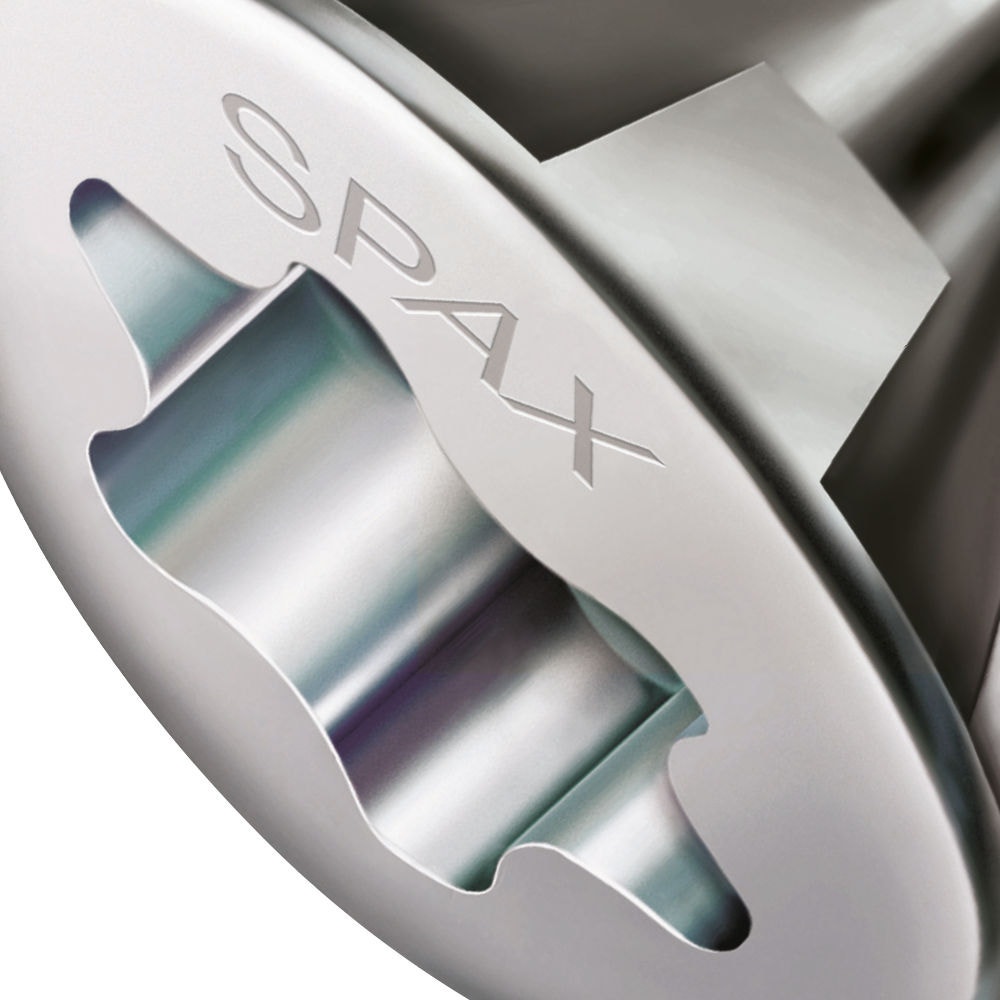
2. This force attack (see picture), which is also referred to as double cross, is a further development of the simple cross force attack of the company Phillips. The difference is that the four flanks of the screwdriver blade do not taper towards the tip. This reduces the cam-out effect somewhat. That is why the cross slot Z is a force attack frequently used at SPAX.

In contrast to a countersunk screw, the lens head has a flat, lenticular head geometry. Due to the special, decorative shape, this is often used for visible, decorative screw connections of furniture or baseboards.
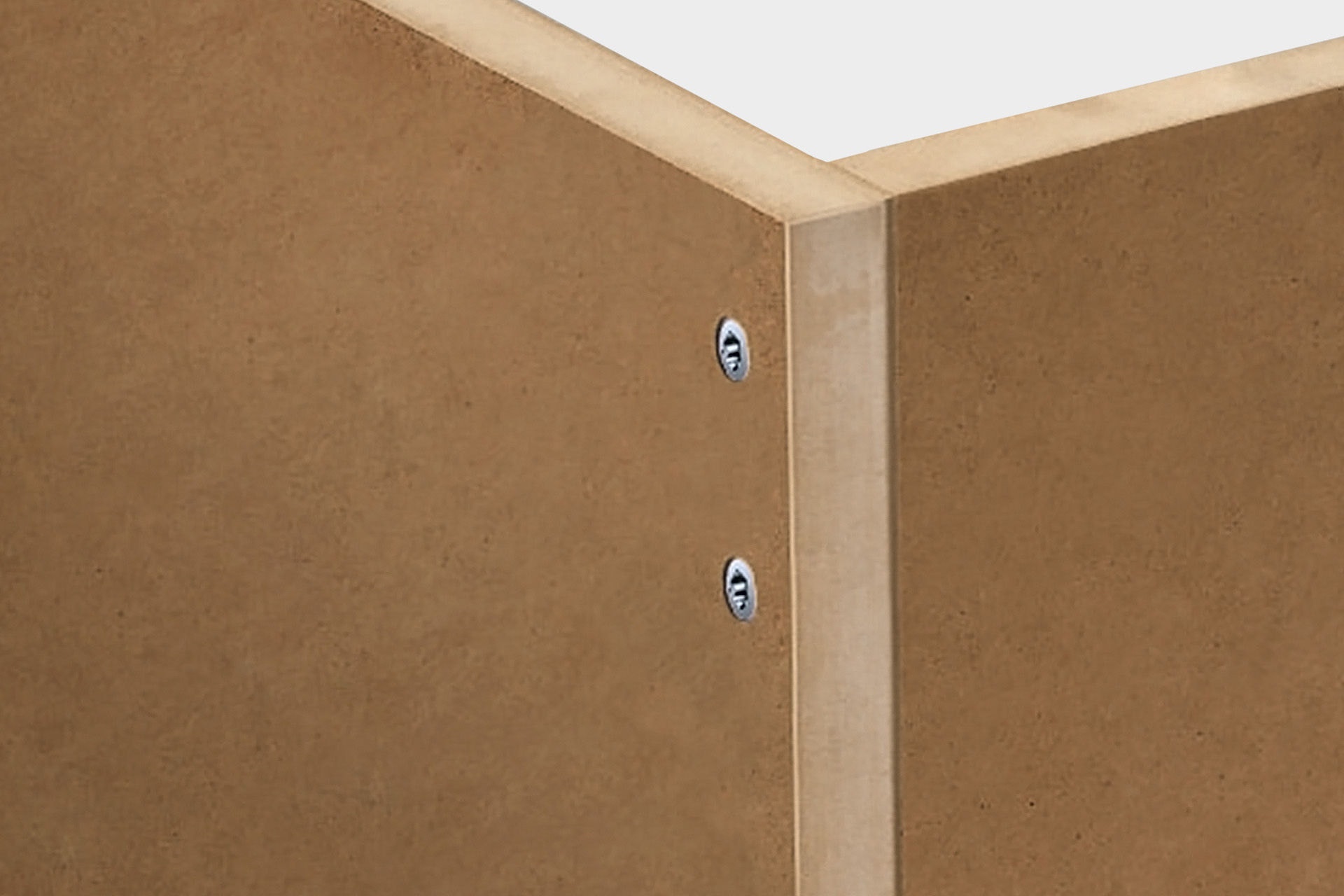

The term MDF is the short form for the term "medium-density wood fibreboard". The name derives from the fact that the density of these panels lies between that of sawn timber and that of wet fibreboard (HDF). MDF boards are used in interior and roof fittings. MDF boards are used for cabinets and cabinet systems and for some years now also in powder-coated form as table and cover panels. They are also often used in high-quality loudspeaker construction due to their high bending and tensile strength. MDF can be treated in a variety of ways with paints and varnishes, creating a smooth, clean surface with profiled edges, cut-outs, etc.
A needle tip is characterized by a steeper and longer shape of the screw tip. It is intended to enable a targeted and precise approach. In addition, it ensures a quick bite in metal and plastic profiles.
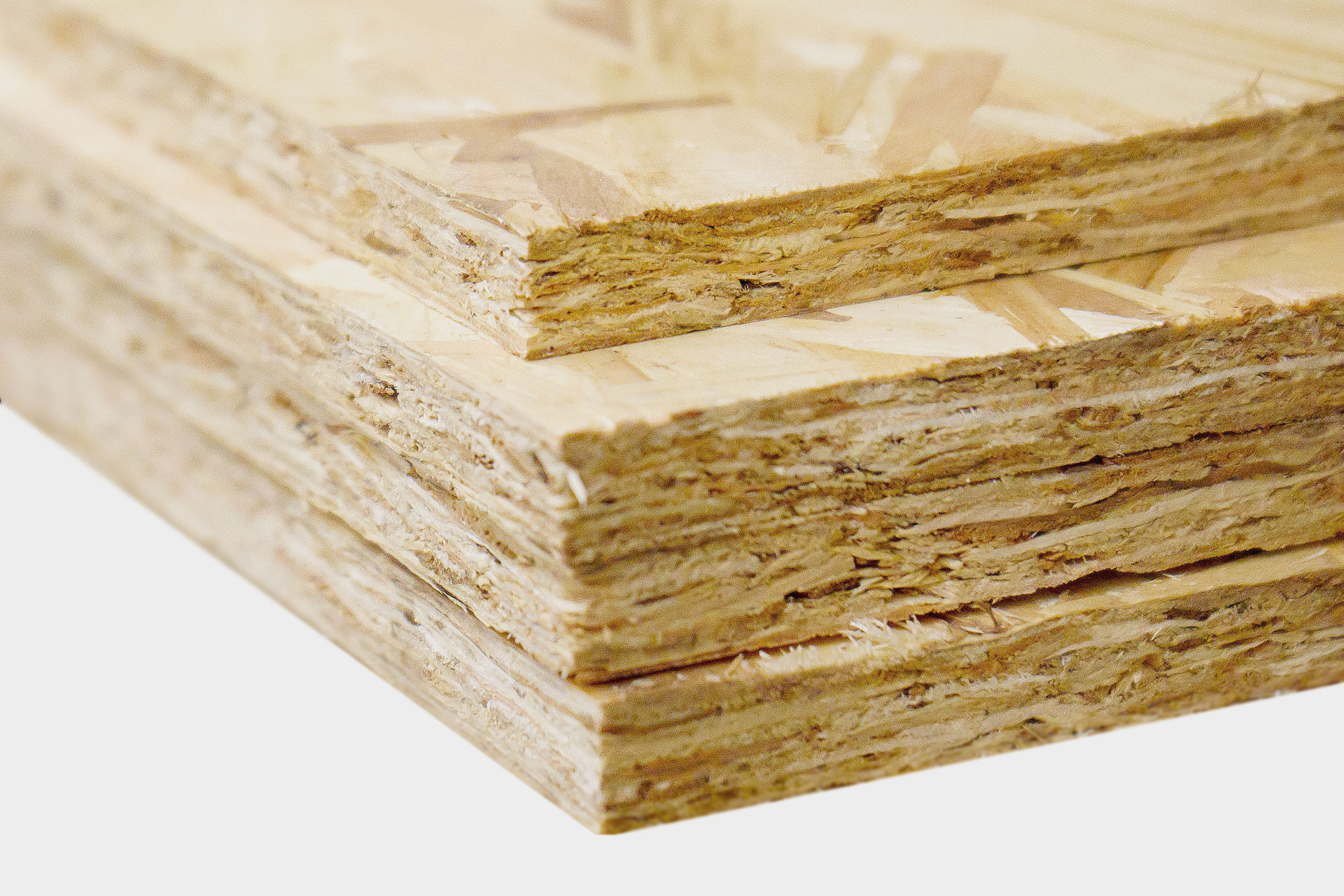

OSB is derived from the English term "oriented strand (or structural) board" and refers to a wood-based board consisting of long, aligned chips. OSB boards are used in many ways in the construction industry, for example as wall, ceiling and floor planking. Due to their long chips, the degree of their flexural strength is higher than that of normal flat pressed boards (chipboard).
Phosphating is a process that is mostly used for steel. This refers to the application of a well-adhering phosphate layer. Phosphated screws (GIX) are mainly used in drywall construction (plasterboard or gypsum fibreboard). Galvanized screws are not compatible with the gypsum putty used in drywall.
The bulk density determines the dead load of the building material. Wood contains different amounts of water, depending on whether the trunk is freshly cut, has already dried a little after cutting or whether the wood for the living space has been dried to wood equalizing moisture. Wet wood is the heaviest. Since the mass of the wood depends on the water content of the wood, the bulk density is a wood moisture-dependent value.
The bulk density provides information about the ratio of cell wall substance to the cavity in the wood. It is a ratio that must be calculated. The bulk density "p" of wood-based and wood-based materials is the ratio of the mass "m" to its volume "v".
Bulk density = mass of wood / volume of wood = kg/m³
Examples based on a wood moisture content of 12 percent to 15 percent:
Balsa wood 90–260 kg/m³, spruce 430–470 kg/m³, Bangkirai 650–1,160 kg/m³, Ipe 950–1,150 kg/m³ (ironwood)
However, the range of the bulk density is also based on the location and environmental factors of the wood, such as the origin of the tree (e.g. Asian continent).
The differences in gross density within a wood species are recognizable by the different annual ring widths of the wood.

The rear wall head is a flat-resting head, which in practice is often used in the furniture industry for fixing hardboard on the back of cabinets and shelves. The flat, plate-like head of the screw is space-saving and increases the contact surface on the fiberboard. The head is not so easy to pull through the wooden plate. The rear wall head is available in the SPAX range up to a thread outer diameter of 5 mm.

The letters of the SPAX brand refer to a "chipboard screw with force attack cross slot  ". The SPAX was first launched in 1967 and has since developed into a world-renowned brand product of the highest quality, made in Germany. The SPAX is now available as a universal screw in many different forms and as a special screw for a wide variety of applications.
". The SPAX was first launched in 1967 and has since developed into a world-renowned brand product of the highest quality, made in Germany. The SPAX is now available as a universal screw in many different forms and as a special screw for a wide variety of applications.
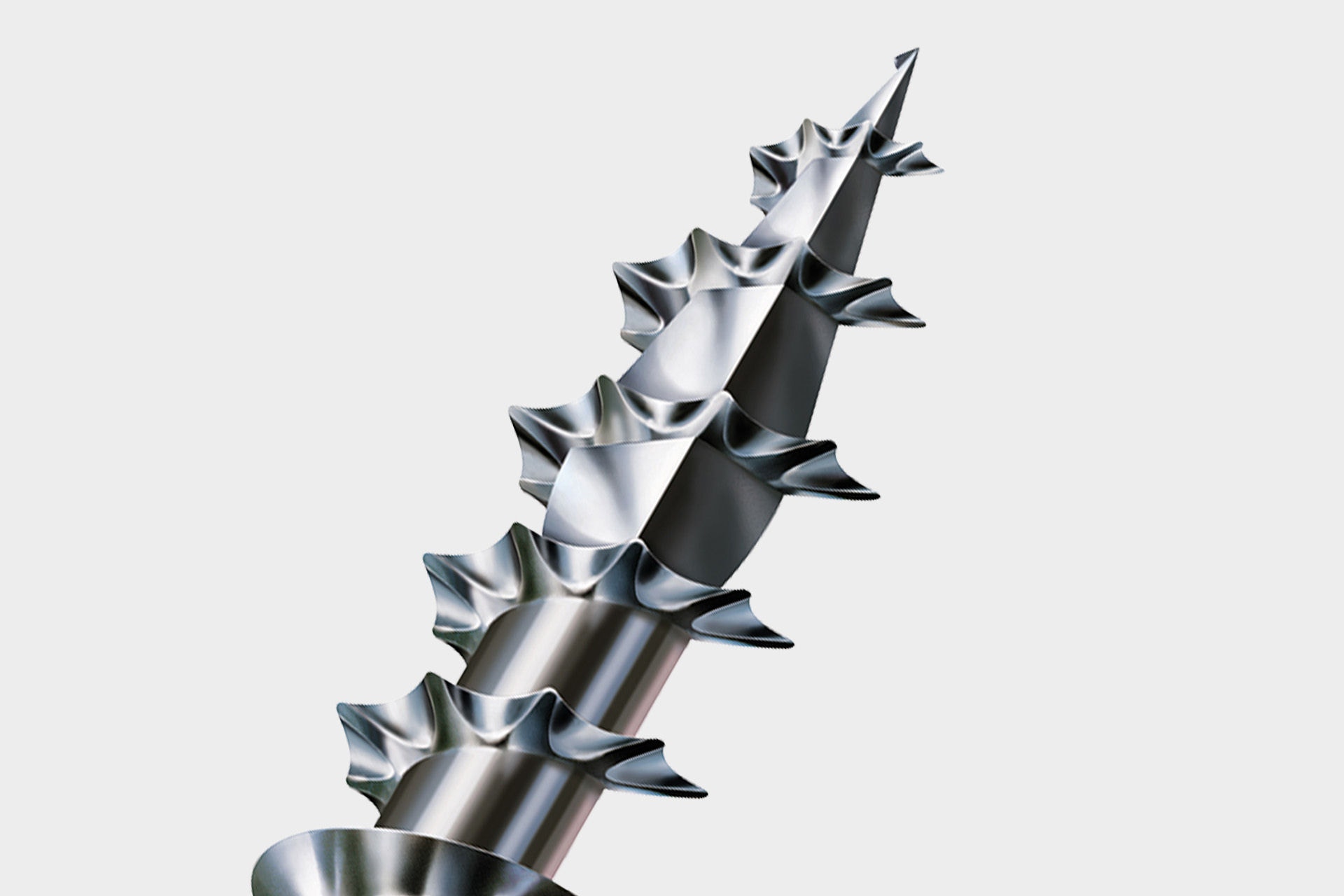

The 4CUT tip allows screwing without pre-drilling (depending on wood). This is achieved by the special screw tip. The square displaces the fibres of the wood and ensures fast gripping. This effectively prevents splicing of the material and reduces the screw-in torque. For hard woods, we recommend pre-drilling with 4CUT as well with SPAX.

Mills in wood – brakes on metal
The MULTI head has recessed pocket segments. Edges thus form between the individual segments, which develop a milling effect when they hit wood. The head is sunk clean and flush. If a SPAX with MULTI head is used to attach a metal fitting, the non-recessed surfaces stop the screw when placed on the metal fitting. This effectively prevents overtightening of the screw and creates a solid connection between the metal fitting and the component. The surfaces are not damaged.
The tip of a SPAX-S is characterized by a shaft profile in the front thread flanks. The thread, which is shaped into the tip, grips quickly and the screw does not slip on hard surfaces, such as coated chipboard. This enables fast work without damaging the workpiece.
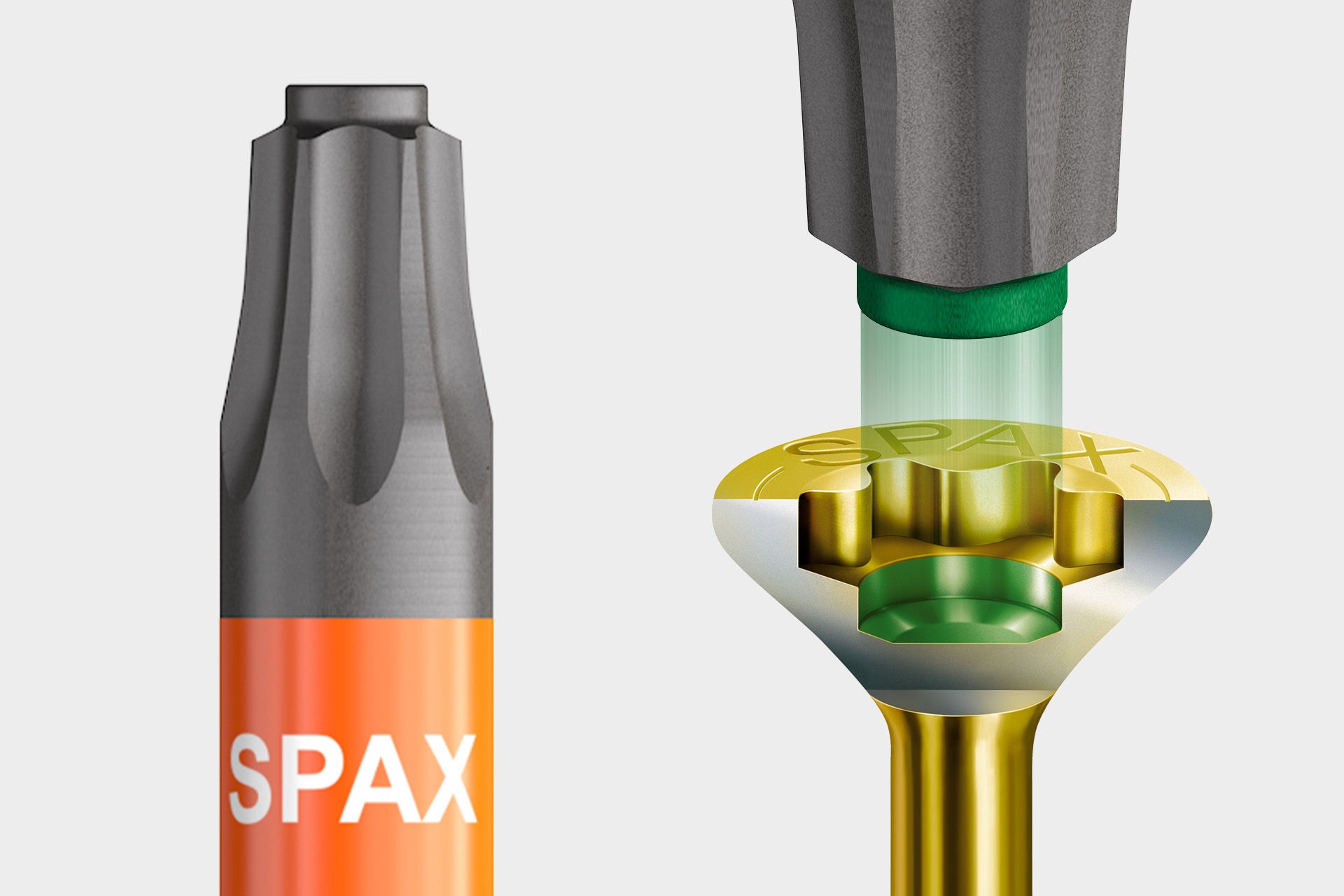

The T-STAR plus force attack offers all the advantages of the T-STAR force attack (no cam-out effect, minimization of pressure force, absorption of high torques). In addition, this force attack has a small recess in the screw head below the drive surfaces, into which the matching T-STAR plus BIT with guide pin can be inserted exactly. This T-STAR-plus connection ensures optimum power transmission, long service life of the T-STAR plus BITs and a perfect fit fit. Even processing SPAX overhead is possible without any problems, as the screw is guided much better and can no longer fall off the BIT.
At SPAX, the hexagonal head is only used for the threaded rods. This makes it possible to better absorb and process the large forces generated during screwing. It thus ensures a high power transmission and can be tightened very well by means of torque. The waistband formed in the lower part of the head ensures a secure fit of the key as it prevents slipping.
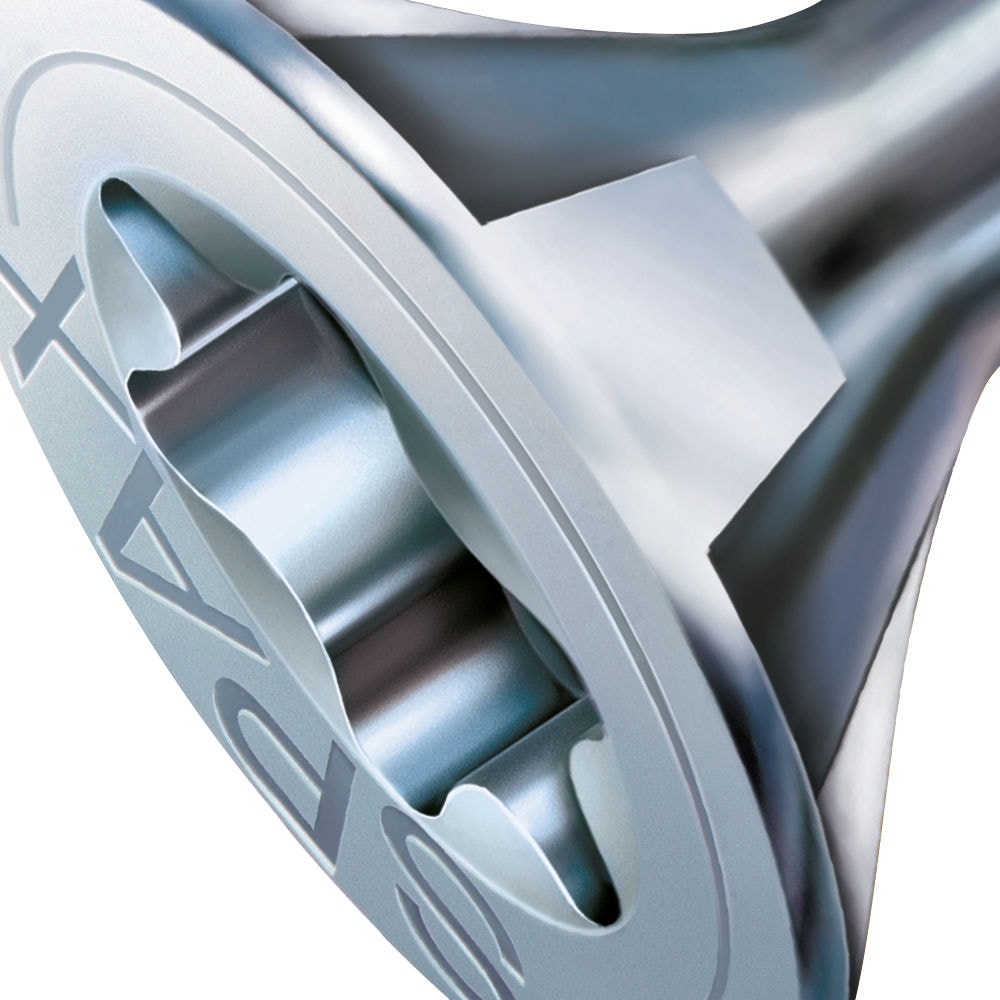

The countersunk head (or flat countersunk head) is the most commonly used head geometry. This has a conical shape and is pronounced in SPAX as a 90° MULTI head. It can be optimally immersed in wood materials and closes flush with the surface.
The chipboard or flat pressed board, is a wood-based material pressed from small wood chips. It is often used as a cheap carrier material for a higher quality surface such as real wood veneer or HPL. They are available both as raw particle board and directly with a surface coating. It is characterized above all by the price and the property that, unlike solid wood, it hardly warps at all.
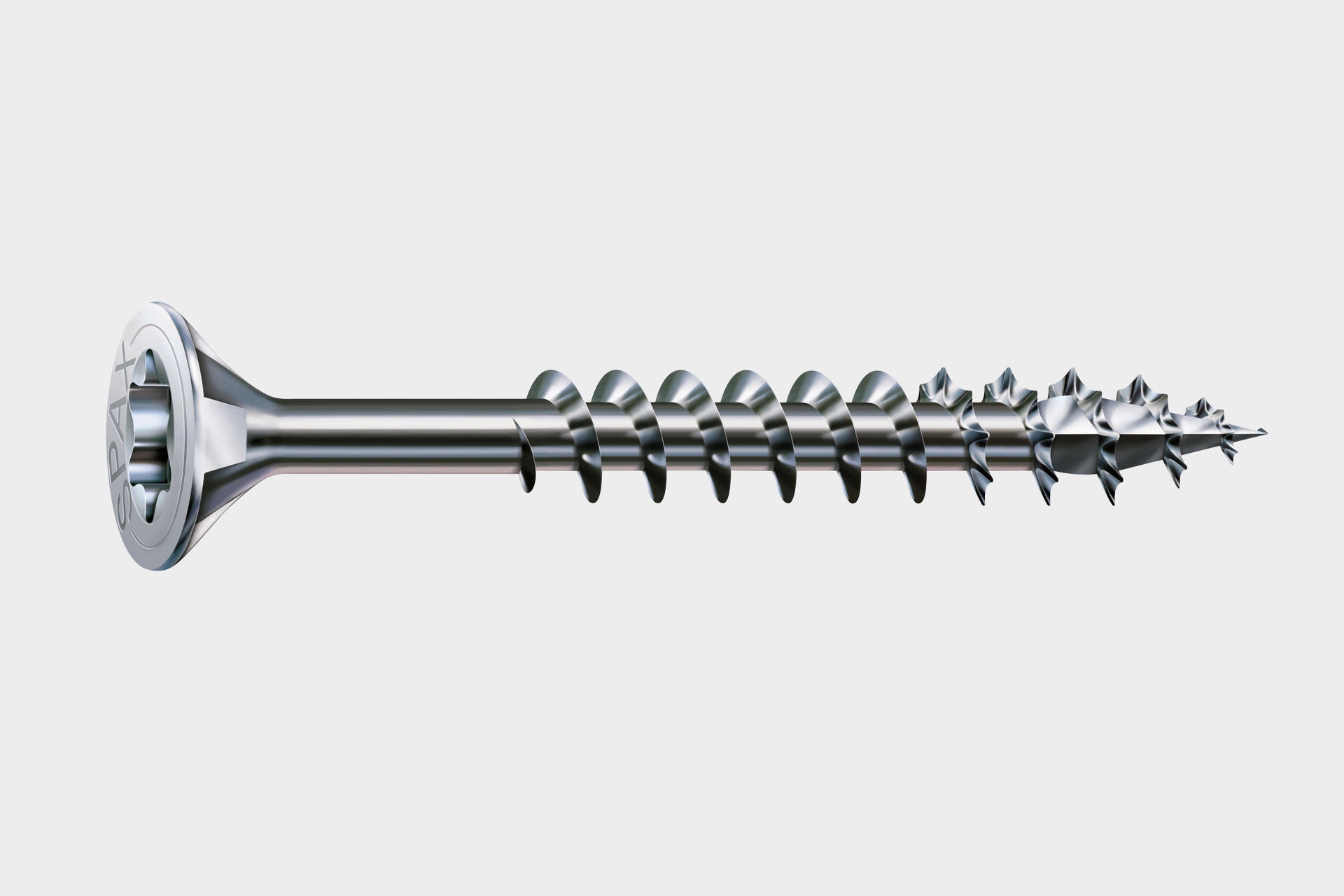
The partial thread extends only a part of the screw length. Partially threaded screws are particularly suitable for attaching wooden panels to wooden beams. The thread-free part should always be chosen so that it corresponds at least to the thickness of the plate to be screwed. The thread tightens in the lower piece of wood, while the upper piece of wood is tightened to the lower one via the screw head.
For SPAX up to 100 mm screw length, the following rule of thumb can be used to calculate the required screw length for the connection of two timbers, for example in terrace construction:
The screw length (Ls) depends on the deck board thickness (t).
Formula: Ls = 2.5 x t
Example: Ls = 2.5 x 24 mm = > Ls = 60 mm
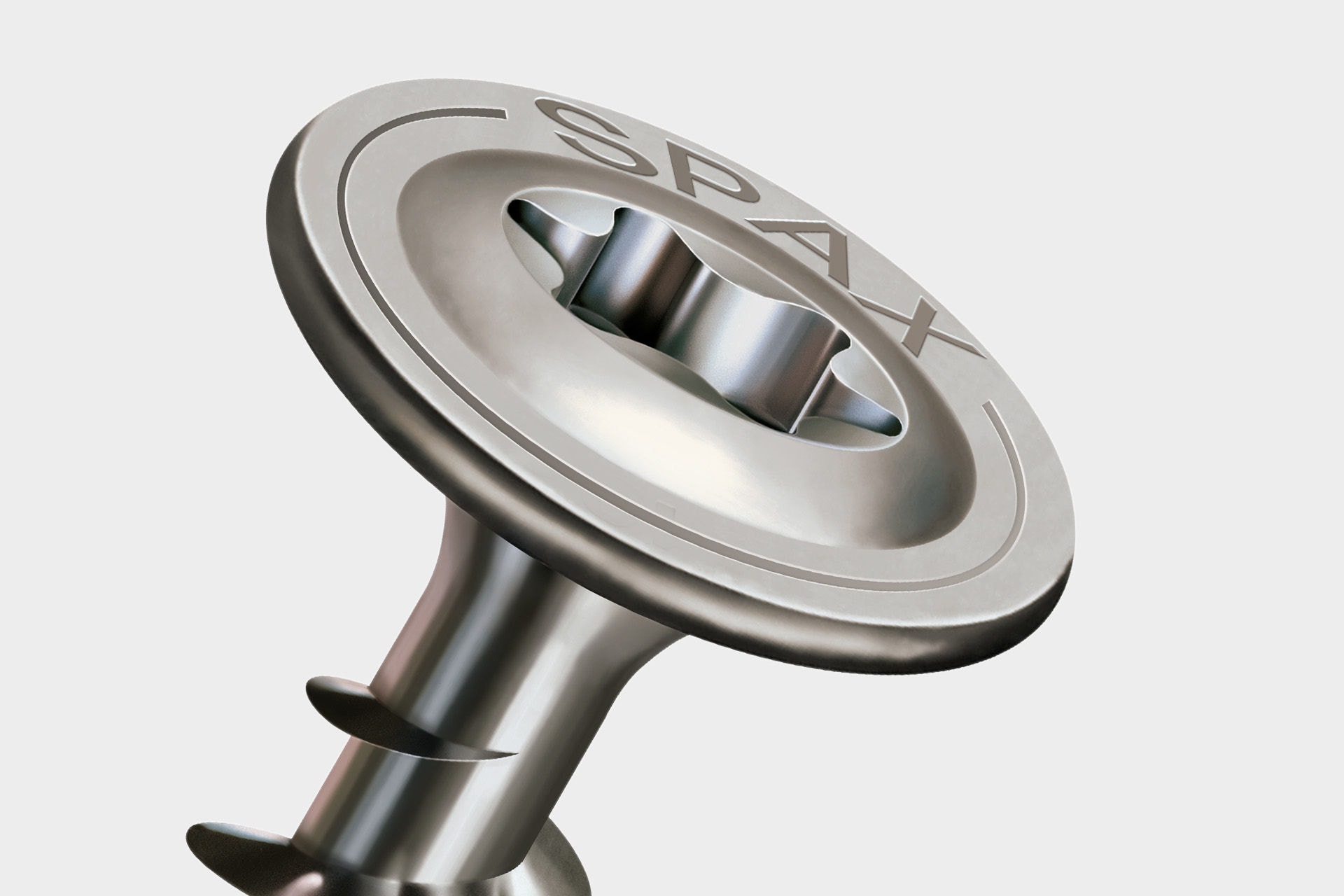

The plate-like head of the screw increases the contact surface on the workpiece and thus guarantees significantly higher head pulling forces compared to a countersunk screw. For example, the SPAX disc head enables better sealing of the wood. The disc head is available in the SPAX range from a thread outer diameter of 5.0 mm.
The trumpet head only finds itself with a few screws. He is mainly used screws for interior construction / drywall construction and the fastening of plasterboard. The special feature is reflected in the concave expression below the head, which ensures a gentle and at the same time powerful contact pressure.
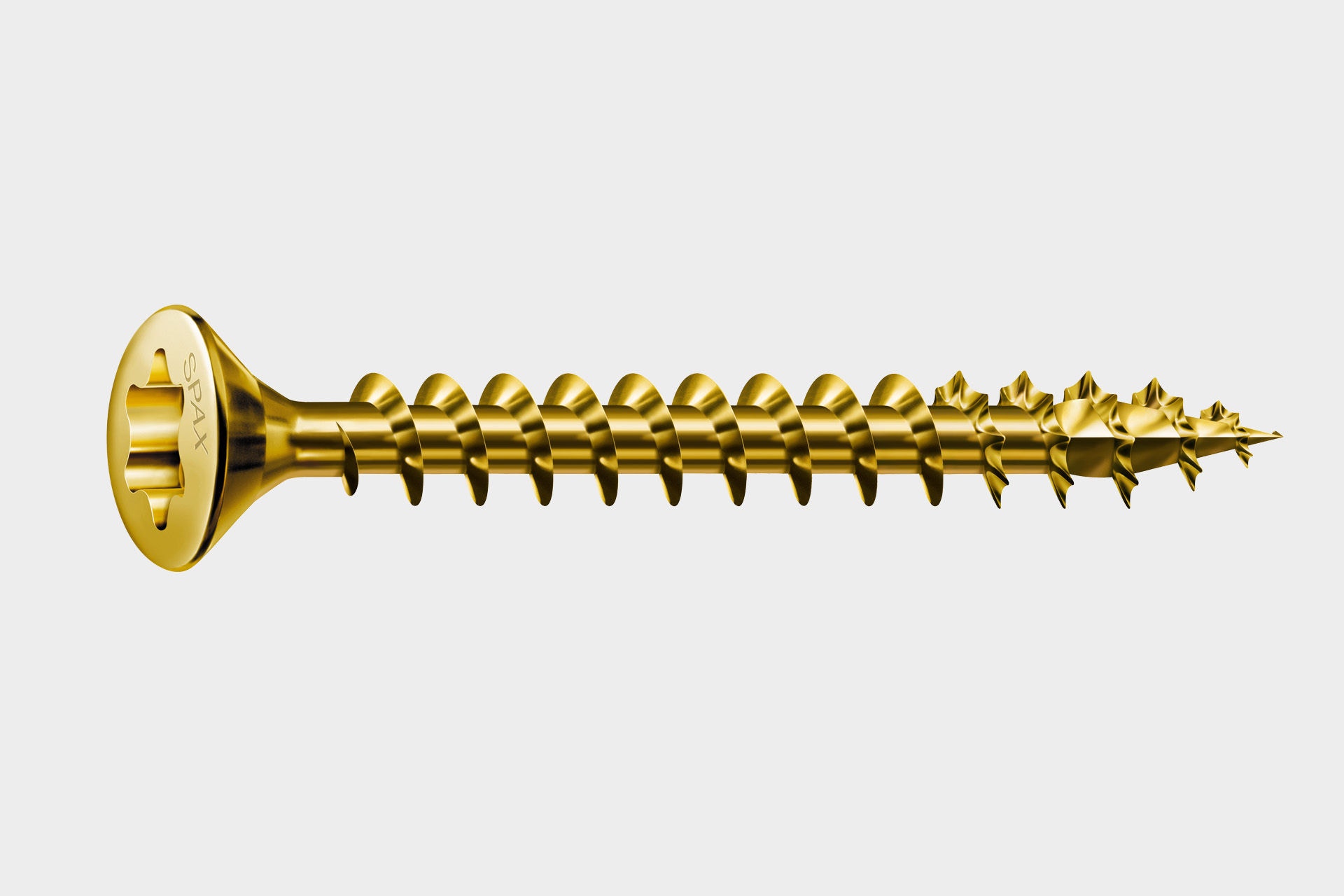

The application of a brass alloy avoids production from brass and thus meets aesthetic requirements while maintaining the usual screw-in properties. Pure brass screws would not meet our quality requirements because brass is too soft as a material. Whether a screw is brass-plated or made of brass can also be tested using magnets: brass-plated = magnetic / brass = non-magnetic . We recommend the application only indoors.
Nickel-plated: The application of a nickel alloy protects the material of the screw from corrosion and at the same time gives it a chrome-colored, slightly yellowish appearance. We recommend the application only indoors.

A) Galvanized, yellow chromated (in common parlance "yellow passivated")
B) Galvanized, transparent passivated (in common parlance "galvanically bright, galvanized")
1. Applying a layer of zinc protects the material of the screw from corrosion and at the same time gives it a grayish, silver-colored appearance.
2. The application of a passivation or chromating layer on the galvanized surface of a screw results (depending on the chemical process) in a yellowish or transparent coloration of the metal. Corrosion protection is increased by passivation or chromating of the zinc layer.
3. After galvanizing and passivation or chromating, the screws are given a sliding coating that reduces the screw-in torque so that the screws are easier to process. SPAX with galvanized surfaces are to be used indoors. They should not be used outdoors and in damp rooms.

The full thread partially extends over the entire length of the screw. Fully threaded screws are particularly suitable for absorbing very large tensile and compressive forces in joints or for reinforcing wooden components.
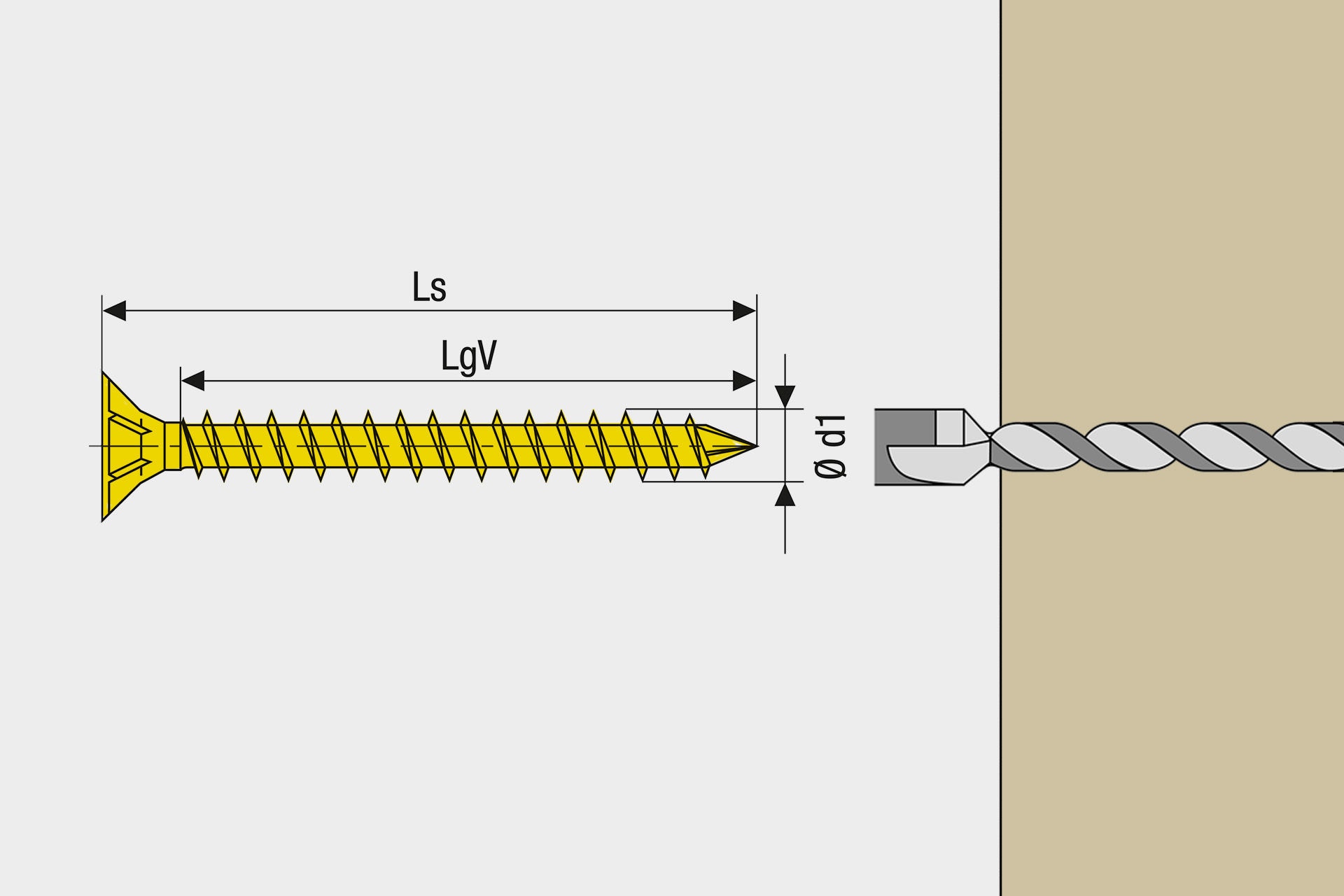
Pre-drilling is the drilling of a hole in the workpiece that has a smaller diameter than the screw. Pre-drilling creates space for the screw in the material and thus prevents the workpiece from bursting. Pre-drilling is a time-consuming step that can be effectively avoided by using a SPAX with shaft profile and 4CUT (depending on the wood). The annoying pre-drilling is eliminated (depending on the wood), as the special 4CUT cleanly displaces the fibers of the wood and thus prevents splintering and splicing of the wood even at small edge distances. It should be noted that pre-drilling is always recommended for very hard woods.
Pre-drilling diameter for SPAX in softwood and hardwood:

* currently not regulated by a general technical approval ** not used in Germany
Coniferous wood: fir, spruce, larch, pine, Douglas fir
Hardwood: oak, beech

WIROX: The surface with extremely high corrosion protection.
The new, exclusive WIROX coating from SPAX offers higher corrosion protection in the neutral salt spray test than with conventional bare galvanizing according to standard and has a significantly higher surface hardness. This makes it ideal for outdoor use in buildings such as carports or pergolas, where they are not exposed to direct weathering. WIROX also has a significantly higher surface hardness than , for example, conventional yellow galvanizing or zinc flake coatings and is therefore more resistant to mechanical stress.
The advantages and properties of the WIROX surface offered worldwide exclusively by SPAX at a glance:
- WIROX achieves higher corrosion protection compared to bare galvanizing
- WIROX offers particular advantages in processing in usage class 2 according to Eurocode 5 for open structures without direct weathering such as carports or pergolas
- WIROX is chromium(VI)-free and therefore significantly more environmentally friendly than conventional surfaces both in production and use
- WIROX is abrasion-resistant and mechanically more resilient
- The zinc layer thickness has been increased by 25% and is now 10 μm – thus the screws correspond to class T2/C2nw according to EN 14592
- Despite WIROX's high corrosion resistance, stainless steel cannot be replaced.
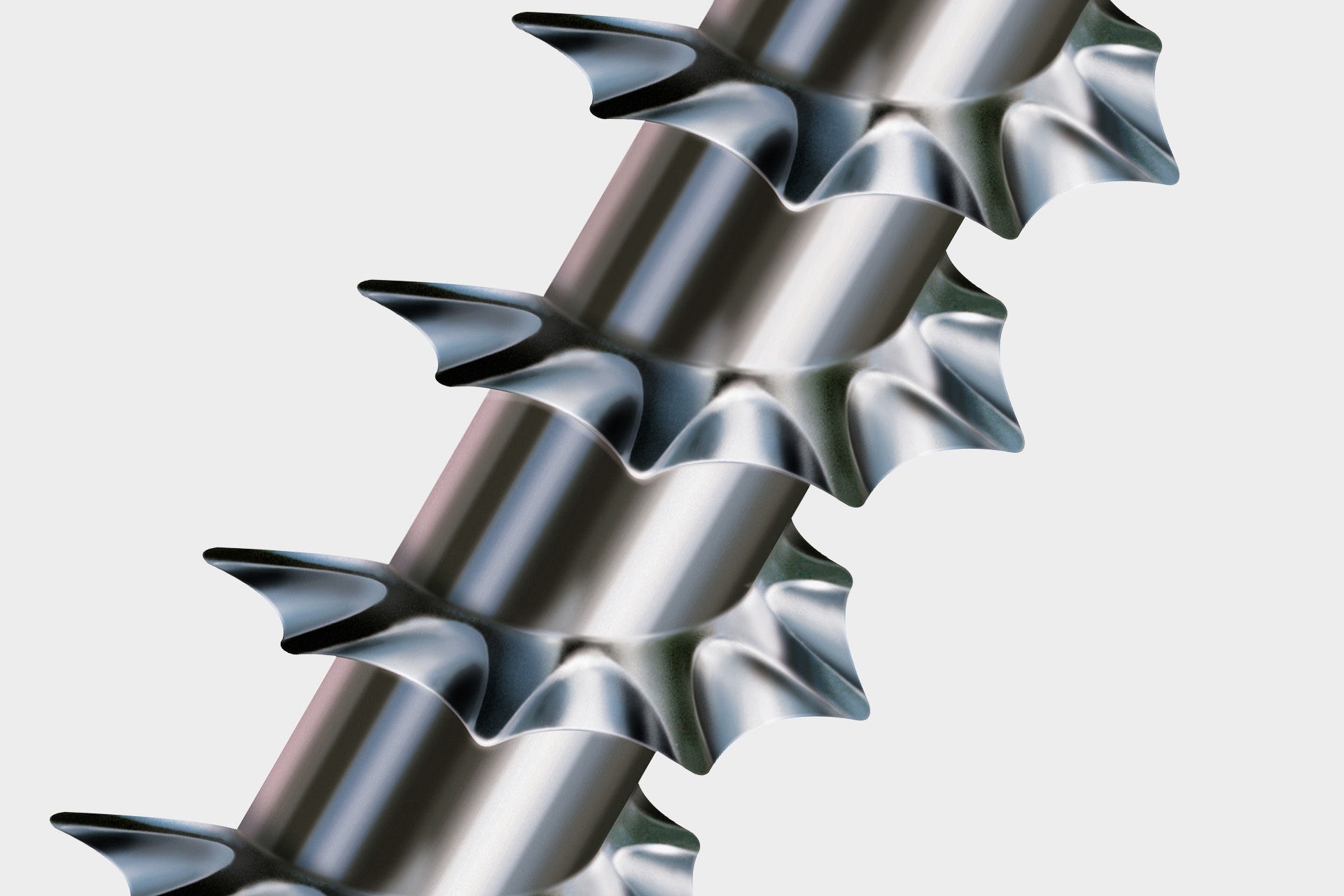
The advantage of a thread with a shaft profile compared to a conventional thread is that it can cut through the fibers of the material more easily. This works similarly to a serrated knife, which offers the same benefits when cutting a tomato, for example. The shaft profile on the thread of the SPAX in combination with the 4CUT allows processing without pre-drilling (depending on the wood)!

YELLOX: Resistant yet good for the environment.
YELLOX is chromium(VI)-free.
YELLOX is chromium(VI)-free and therefore more environmentally friendly than the usual yellow galvanizing. And that both in production and in use. Nevertheless, it is also more resistant to corrosion than conventional bright or yellow galvanized screws. YELLOX is an innovation that benefits the environment and the user.
The advantages and properties of the YELLOX surface offered worldwide exclusively by SPAX at a glance:
- With YELLOX a higher corrosion protection is achieved, compared to bare galvanizing with the same surface layer thickness.
- YELLOX is chromium(VI)-free and therefore significantly more environmentally friendly than conventional surfaces in both production and use.
- With YELLOX also in the future a yellowish appearing screw, with increased corrosion protection and chromium(VI)-free (ie environmentally friendly and without health concerns), screw together.

The SPAX with cylinder head is easy to sink into the wood and, thanks to the small head diameter, enables almost invisible screwing. Due to the low splitting effect when sinking the head, SPAXs with cylinder heads are particularly popular in timber construction or terrace applications.

